New Publication in Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications
8 January 2024, by Website Team Biologie
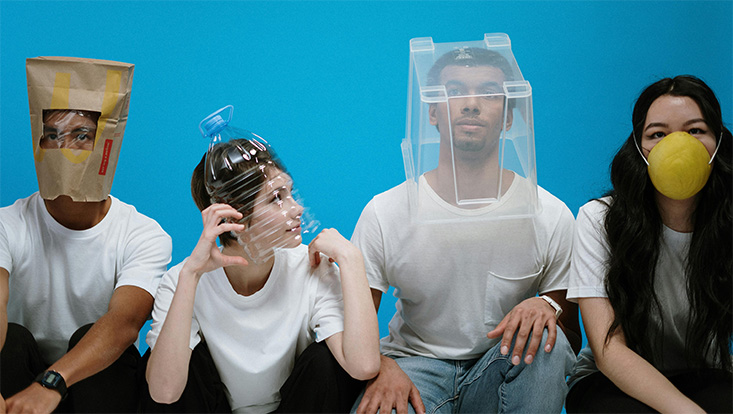

Photo: pexels.com
Face masks were a key measure in controlling virus transmission during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previous research shows that masks affect various aspects of social cognition, such as emotion recognition and social evaluation. In our project, we conducted two experiments with 311 participants to examine the tendency for social avoidance toward masked and unmasked individuals. The results showed that participants were more willing to approach masked faces, which was linked to individual differences in perceived pandemic threat. While the absence of a mask could lead to conscious social avoidance, automatic behavior regulation remained unaffected, suggesting the relative robustness of reflexive behavioral patterns in the face of changing social norms.